Is pyrolysis better than gasification?
The United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP) says global solid waste will increase from 2.3 to 3.8 billion tonnes between 2023 and 2050.
Industrial production and consumption patterns create ever-increasing waste, now considered a planetary crisis on par with climate change and biodiversity loss. Fortunately, we can solve multiple waste challenges by treating end-of-life products as resources instead of waste.
Recovering materials and inherent energy from end-of-life products limits natural resource extraction, pollution, and climate change — protecting our environmental health.
In this article, you will better understand pyrolysis vs gasification, and how they are similar (and different).
Subscribe to the Contec Monthly on our LinkedIn Page and gain relevant insights into circularity and sustainable business models.
What is (tire) pyrolysis?
Pyrolysis is a thermochemical process for recycling end-of-life tires (ELTs) and plastic, industrial, and agricultural wastes.
It breaks down carbon compounds in solid materials at high temperatures of 300 to 850°C in an oxygen-free atmosphere. The lack of oxygen prevents combustion but decomposes complex carbonaceous material into simpler products.
According to Shah and others (2023), the pyrolytic products are as follows:
- Solids account for 20-50 per cent of the products as char, which contains residual solids from the feedstock, and ash.
- Liquids (30-50 per cent) like tar and oil as a mixture of aromatic hydrocarbons. The heating value is 5-15 MJ/kg.
- Syngas (20-50 percent) is a mixture of methane, carbon dioxide, carbon monoxide, hydrogen, and other volatile compounds. The heating value of this low calorific gas is 3-12 MJ/Nm3.
The pyrolysis process is endothermic and requires heat, which, as in Contec’s tire pyrolysis plant, is provided by the pyrolytic gas (which contains the basic components of syngas). When treated through pyrolysis, ELTs yield tire pyrolysis oil (TPO), recovered Carbon Black (rCB), pyrolytic gas, and recovered steel.
Pyrolysis of ELTs achieves a large reduction in waste, with little or no pollutants and emissions. However, pyrolysis isn’t the only thermochemical solution available for recycling.
What is gasification?
Like pyrolysis, gasification is also a thermochemical treatment. Through gasification, carbonaceous materials are partially oxidised into mainly gas products.
The oxidising agents can be oxygen, air, steam, or mixtures of these gases. According to Shah and others (2023), temperature can reach 800 to 1100°C when air is used as the agent. When pure oxygen is the gasification agent, temperatures can get as high as 1500°C.
Gasification can treat solid wastes like agricultural, industrial, municipal, and oily sludges, as well as, ELTs and coal.
Pyrolysis is a necessary preceding step for gasification, as the complex hydrocarbons produced through pyrolysis, such as char, tar/oil, and gas, act as gasification feedstocks. Gasification heats pyrolytic char and tar to even higher temperatures, further breaking them down into methane, carbon dioxide, carbon monoxide, and hydrogen.
The product profile of gasification, according to Shah and others (2023), is as follows:
- Solids account for 30-50 per cent of input weight and comprise metals and inorganic elements.
- Liquids (10-20 per cent) are oil and tar.
- Syngas (30-60 per cent) has high carbon monoxide and hydrogen fractions and more carbon dioxide than pyrolytic gas. The oxygen, as a gasification agent, produces syngas with a low heating value of 3-12 MJ/Nm3, while steam yields syngas with higher heating values of 10-14 MJ/Nm3.
Gasification is part of the pyrolysis process, but the similarities don’t end here.
Pyrolysis vs gasification: common points
The similarities in pyrolysis and gasification often cause people to confuse the two processes.
- Both are thermochemical processes that break down complex solid wastes into simpler compounds.
- Both produce valuable energy-dense products, such as syngas, bio-oil, and char, that can be used as fuels.
- Gasification and pyrolysis, as recycling processes, reduce solid waste volumes and recover energy and materials with minimal pollution and carbon emissions.
That said, these are two different thermochemical processes, often used to achieve different results.
Let’s look at how they differ.
Pyrolysis vs gasification: differences
Despite the similarities between them, pyrolysis and gasification are different processes. Some of the main differences are:
- Pyrolysis occurs without oxygen, while gasification is a partial oxidation process that requires oxygen as a gasification agent.
- Pyrolysis temperatures are far lower than those used in gasification.
- Gasification is always preceded by pyrolysis, acting only on the pyrolytic products. However, pyrolysis doesn’t need to be followed by gasification.
- According to Durak, gasification can be combined with carbon capture and storage technologies to handle emissions, making it more environmentally conscious than pyrolysis alone.
- Pyrolysis is better for treating plastic waste, as tar formation during gasification is an operational challenge that reduces gas yield.
- Input materials significantly influence the composition and amounts of pyrolysis products, but this matters less in gasification, as it’s limited to differences in tar and char.
Which is better: pyrolysis or gasification?
Pyrolysis and gasification can have a low environmental impact.
- Due to incineration’s high pollution and emissions, pyrolysis and gasification can be an alternative to waste-to-energy technologies.
- Both processes can significantly reduce landfilling and associated pollution problems.
- Both processes can offer decentralised local solutions compared to landfilling or export.
According to Durak, pyrolysis and gasification each have strengths and weaknesses.
The choice of the recycling method depends on waste/feedstock availability, cost, and composition, as well as energy requirements, equipment availability, target products, and objectives of the waste treatments.
- Each process produces syngas for electricity generation and char used for soil amendment.
- The syngas from gasification are made into methane or liquid after further conversion to produce transportable and storable fuels. Pyrolysis oils, after refining, are used as liquid fuel or for electricity generation.
- The liquid fuel from both processes acts as feedstock: gasification products are used to make fertilisers, while Tire Pyrolysis Oil is used to manufacture virgin Carbon Black.
- Pyrolysis char is processed into rCB, an alternative to fossil-based tire fillers.
Pyrolysis can produce more energy per unit of waste treated than gasification. Gasification, on the other hand, can produce fuels from coal.
Tire pyrolysis at Contec
Pyrolysis and gasification can be used in sustainable manufacturing to reduce global dependence on fossil fuels for energy, fuels, and feedstocks. Commercialisation of the two technologies is underway.
Contec has one of less than five commercial pyrolysis plants in the European Union. The plant processes ELTs using a proprietary molten salt technology, Molten®, which Contec developed to make the process efficient and reduce safety problems commonly associated with pyrolysis. Contec uses a proprietary pyrolysis process to turn end-of-life tires into new commodities. Learn more about our process.
If you liked reading this article, we recommend the following content:
The countdown to the completion of our plant expansion work in Szczecin is well underway!
“We’ve achieved further milestones related to the construction of our plant, for which I would like to express my deepest gratitude to the entire team involved in the work. Their dedication and hard work have been instrumental in reaching these milestones”, said Dominik Dobrowolski
Huge shoutout to PROCHEM for their unwavering support throughout this entire expansion journey! Your partnership has been invaluable.


If you liked reading this article, we recommend the following content:
Our support to the Great Orchestra of Christmas
Exciting Announcement!
Our company proudly supports the annual finale of The Great Orchestra of Christmas Charity (Wielka Orkiestra Świątecznej Pomocy) in a special way. 🎉 Renowned journalist and science promoter, Tomasz Rożek, and talented actress Julia Kamińska have created artistic abstractions using our rCB! 🔥 It’s the first-of-its-kind collaboration in the history of rCB, and we’re thrilled to be part of this historic moment. Moreover, all auction proceeds will support the treatment of lung diseases post-pandemic. 🫁 We strongly encourage you to be a part of this significant initiative!
Join us in making a difference! 💪🏽 Bid now:

* Wielka Orkiestra Świątecznej Pomocy is a charitable organization in Poland that conducts an annual Grand Finale fundraiser to support medical care for children and adults. In 30 years of its charitable endeavors, the organization has raised nearly PLN 2 billion and donated 71,500 pieces of medical equipment.
Pyrolysis vs. incineration: turning waste into resources
Incineration is the most widely used waste-to-energy process.
However, innovative technologies like pyrolysis are gaining increased attention for being better for the environment. Tire pyrolysis is a technology that produces synthesis gas (syngas) and tire pyrolysis oil with various applications.
In this article, you can compare pyrolysis vs incineration to determine if pyrolysis is a better circular solution for your means, especially for reducing waste streams like end-of-life tires.
Subscribe to the Contec Monthly on our LinkedIn Page and gain relevant insights into circularity and sustainable business models.
What is (tire) pyrolysis?
Pyrolysis is a form of thermal decomposition of carbon-containing substances, such as end-of-life tires (ELTs), wood, biomass, and plastics, when heated to high temperatures between 400 to 1000°C without oxygen. Lack of oxygen prevents combustion and allows complex carbonaceous material to decompose thermally into simpler products: low- to medium-calorific-value gases; liquids, oils, or tars; and solid char.
ELTs thermally decomposed through pyrolysis break down into syngas, pyrolysis oil, and char. This waste-to-energy technology can transform low-energy density materials into high-energy-density biofuels and high-value chemicals. The proportion of gas, liquids, and solids produced can be varied by changing the heating rate or temperature.
Pyrolysis reduces up to 100 per cent of waste in terms of weight and volume and can produce transportable and storable fuels. Moreover, the emissions and other pollutants released by pyrolysis are little or negligible.
What is (tire) incineration?
Incineration is the combustion of solid organic materials, like tires, in the presence of oxygen at very high temperatures, 850 to 1000°C. The process produces heat, flue gas, and ash.
Incinerators are generally large-scale and connected to steam boilers heated by combustion to produce hot steam that turns turbines to generate electricity. The partially cooled steam after rotating the turbines serves as a heat source for buildings or industrial uses. The process is inefficient; not all of the heat produces steam. Some heat is lost through flue gas and ash.
The ash is residual or bottom ash from combusted materials and fly ash from incombustible materials. The ash is a waste and has to be landfilled.
The flue gas from incineration contains carbon dioxide, water vapour, and nitrogen produced by burning carbon compounds. Depending on the material combusted, flue gas can also contain toxic pollutants like particulate matter, sulphur dioxide, nitrogen oxides, hydrogen chloride, dioxins, furans, and heavy metals like mercury and cadmium, which are hazardous to health.
Incineration decreases waste volumes by 80 – 90 per cent and helps reduce methane and other pollutants produced at landfills. By preventing methane production, every ton of waste incinerated prevents the release of one ton of carbon dioxide equivalent into the atmosphere.
Figure 1: An Incineration Plant (Image Credits: Use of Incineration MSW Ash: A Review)
Early incinerators were relatively basic and often burned waste without significant sorting or separating hazardous, bulky, or recyclable materials. Modern incinerators have improved furnace design and processes to ensure complete combustion, presorting of waste, and flue gas cleaning equipment that has reduced incinerator pollution.
Pyrolysis and incineration: what are the common points between them?
To compare these two waste-to-energy technologies, it’s necessary to consider the similarities and differences between incineration and pyrolysis. The common aspects of the two processes are listed below:
- Decomposition of Organic Matter: Both incineration and pyrolysis are methods for breaking down carbonaceous waste into different chemical compounds.
- Thermal processes: Both incineration and pyrolysis are thermal processes where heat is used to treat waste and initiate chemical reactions.
- Production of Gaseous Compounds: Both processes generate gaseous compounds as end products due to organic matter decomposition.Pyrolysis produces syngas, which is collected and used as fuel. Flue gas from incineration is not used and must be cleaned to remove gaseous pollutants and particulate matter before being released into the environment.
- Waste reduction: One of the most vital achievements of both incineration and pyrolysis is significant reduction in landfill waste.
Pyrolysis vs incineration: what are the differences?
While these common points exist, it’s important to note some key differences between incineration and pyrolysis:
- Oxygen requirement: Though both are thermal processes, incineration requires oxygen. Pyrolysis occurs without oxygen in an inert atmosphere, such as nitrogen.
- Temperature: Incineration requires very high temperatures above 850 to 1000°C. In pyrolysis, the process occurs at lower temperatures from 400 to 1000°C.
- Residues: Incineration produces significant amounts of ash as a residue, which is waste and has to be landfilled. The ash is contaminated by toxic pollutants that will pollute the soil. In contrast, the solids produced through pyrolysis are high-value products like char.
- Energy Recovery: Incineration produces energy in the form of electricity or heat generation. Pyrolysis produces transportable and storable biofuels like syngas and tire pyrolysis oil, which can be used as fuel for combustion for industrial purposes and as a partial substitute for diesel.
Why incineration is not a good solution
Incineration has several disadvantages due to its environmental and health impact:
- Incineration reduces recycling: Incineration can compete with recycling for materials, as burning waste may be more cost-effective and convenient than recycling. It discourages recycling efforts and decreases the recovery of recyclable materials.
- Emission of carbon dioxide: Incineration releases carbon dioxide, contributing to climate change. Total greenhouse gas reduction by incineration compared to even landfilling is uncertain. Carbon emissions from incinerating materials like plastics can be higher than landfilling if the incinerator is inefficient.
- Emission of hazardous end products: Incineration produces dangerous byproducts, including toxic flue gases and ash. Recent research in the EU has indicated a high level of harmful pollutants and particulate matter in the environment around incinerators.
- Health risks: Incineration can pose health risks to those living close to incinerators due to exposure to air pollutants and hazardous emissions. Prolonged exposure to these pollutants can lead to respiratory, cardiovascular, and other health concerns.
- Pollutants enter the food chain: Pollutants from incineration can find their way into the food chain, which is a significant concern for public health. For example, dioxin has been found in chicken eggs and vegetables grown in areas surrounding incinerators, making them unsafe for consumption.
Due to the negative environmental and health impacts, public perception and concerns about incineration make it difficult to install new incinerators.
Pyrolysis is better than incineration: here’s how
Pyrolysis is preferable as a waste-to-energy process compared to incineration for many reasons (Ławińska, 2022).
- Efficiency: Pyrolysis is more efficient than incineration as 100 per cent of materials are recovered.
- Versatile system: Pyrolysis can treat various waste streams, including biomass, plastics, and ELTs.
- Emissions Reduction: Pyrolysis creates significantly less carbon emissions than incineration, whose main product is carbon dioxide.
- Health benefits: Pyrolysis doesn’t create toxic pollutants or particulate matter in the products. Therefore, it has no adverse effects on human health. Moreover, no expensive clean-up or dust removal systems are required.
- Low-temperature use: The lower temperatures in used pyrolysis cause less equipment corrosion, lowering maintenance costs. Also, lower temperatures allow for the recovery of ferrous and non-ferrous metals in the solid component.
- Pyrolysis control: It’s easier to control pyrolysis as it’s an endothermic process compared to incineration, which is exothermic.
- Circular and Storeable products: Pyrolysis products can be stored, processed, and marketed later. The creation of recovered pyrolytic products such as gas, pyrolysis tire oil, Carbon Black, and steel makes it more sustainable and suitable for a circular economy.
Pyrolysis is still a relatively new technology compared to incineration, and fewer pyrolysis plants are in operation worldwide than incinerators. The infrastructural gap of pyrolysis plants will be reduced when its cost-effectiveness is worked out.
Tire pyrolysis at Contec
Contec operates one of the EU’s few tire pyrolysis pilot plants in Poland.
The company has developed and integrated a proprietary molten salt technology, Molten®, to make the production process more efficient and minimise the safety risks associated with pyrolysis.
Incineration and pyrolysis share some common aspects, such as the thermal decomposition of organic matter and the production of gaseous compounds. Still, they’re distinct processes, and pyrolysis’ advantages of efficiency, controllable operating conditions, high-value end products, and low environmental impact make it a more sustainable and better choice for the circular economy. Find out more about Contec’s sustainable TPO.
If you liked reading this article, we recommend the following content:
Tire recycling pyrolysis: pros and cons, explained
Tire pyrolysis is an innovative and sustainable solution that treats end-of-life tires (ELTs) as a resource, not waste.
Pyrolysis involves the thermal decomposition of tires in the absence of oxygen, where the vulcanising bonds between the polymers are broken down into valuable byproducts with little negative environmental impact. Since the number of ELTs discarded annually is over one billion and growing, this is a substantial source of feedstock that has the potential to replace fossil fuels in the manufacture of several products.
Tire pyrolysis is not new, but the technology has risen in prominence due to its potential to provide circular raw materials. However, safety concerns and other difficulties are associated with the pyrolysis process.
This article analyses the pros and cons of tire recycling pyrolysis and how Contec, an industry leader, has developed a clean and safe technology that meets all sustainability and safety standards.
What are the pros of tire pyrolysis?
Tire pyrolysis can potentially reduce emissions and increase energy availability and circularity due to some key advantages, as discussed below.
Pyrolysis as renewable fuel/energy
Tire pyrolysis oil (TPO) is the most abundant product of tire pyrolysis since 85 per cent of tire components are petroleum-based.
TPO’s properties are similar to some fossil fuels, making it a highly efficient and versatile energy source. After processing and treatment, TPO can be a sustainable option for partial replacement of fossil fuels in many applications:
- As fuel for motor vehicles, diesel burners, generators, engineering machinery, etc.
- As oil for power generation and heating
- Act as feedstock for the manufacture of medium to low reinforcing virgin Carbon Black
- After distillation, TPO can be used for the production of high-value chemicals.
Renewable TPO can reduce many industries’ dependency on fossil fuels.
Storage convenience
One of the advantages of TPO is the convenience of storing, transporting, and pumping it. Since many forms of renewable energy are challenging to store, the storage convenience increases TPO’s market appeal. Moreover, distilled TPO can be used as fuel with existing machinery without any changes, enabling immediate applications.
Diesel
TPO’s 41–44 MJ/Kg calorific value is similar to diesel’s 45 MJ/Kg calorific value. After distillation and desulphurisation, TPO can be used in a TPO-diesel blend (10 per cent TPO and 90 per cent diesel).
Tire pyrolysis’ byproducts result in sustainable options for the tire industry
In addition to fuels, the tire pyrolysis process generates valuable byproducts, including Recovered Carbon Black (rCB) and steel wire. The rCB is a viable option to replace medium-grade virgin Carbon Blacks from fossil fuels. rCB has proven applications as a circular raw material in many industries, including tires, paints, coatings, inks, and rubber manufacturing.
The recovered steel is recycled without losing quality and used to manufacture steel parts for tires and other industries.
Tire pyrolysis can reduce emissions
A tire pyrolysis plant is the most environmentally responsible approach to waste tire management. Other methods of disposing of ELTs, such as incineration and landfilling, have high carbon emissions.
Tire pyrolysis efficiently converts and recovers materials and energy in waste tires and creates few carbon emissions and pollutants. It produces a renewable syngas byproduct, which can heat the pyrolysis plants, further reducing the process’s carbon footprint.
What are the cons of tire pyrolysis?
Pyrolysis of ELTs into valuable products has disadvantages, including further product processing, safety considerations, pollution concerns, and operational expenses.
These drawbacks should be carefully assessed and managed when implementing a tire pyrolysis process.
No usage as engine fuel
TPO is a heavy, dark fluid whose hydrocarbon composition depends on the pyrolysis process, conditions, and feedstock. According to Han 2023, at temperatures below 500°C, the TPO has more aliphatic hydrocarbons (isoprene and limonene) and fewer aromatic hydrocarbons. At temperatures over 500°C, the aromatic hydrocarbon content increases.
While TPO’s chemical composition is similar to crude oil, high levels of limonene and pollutants like sulphur make it unsuitable for engine fuel use. Heavy oil is only suitable for use as heating fuel. Therefore, TPO requires additional processing and distillation before it can be used as engine fuel.
Pollution
TPO produced from pyrolysis can include pollutants like nitrogen, sulphur compounds, and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs). Pyrolysis using higher temperatures creates more PAHs, which are known to be carcinogenic and mutagenic. Burning TPO can produce gaseous pollutants that are an environmental concern.
In large-scale use of TPO, it’s necessary to have a flue gas purification system to remove these emissions, which can increase operational costs.
Tire pyrolysis can be expensive
The overall cost of a tire pyrolysis plant is directly linked to its efficiency and the technology required to comply with environmental and safety regulations. Higher-efficiency equipment tends to be more expensive. The initial capital cost of building pyrolysis plants can be high and run into millions of euros.
The fuel choice and the need for highly skilled personnel for plant operation will also add to the costs. However, the high value of pyrolytic products is expected to make pyrolysis feasible in the long term.
Safety concerns
Pyrolysis processes have historically suffered from safety issues. The risks associated with pyrolysis involve accidental combustion of organic material due to contact with oxygen or high temperature. Other issues are the need for precise process control, ensuring equipment integrity, and addressing inadequate safety measures to prevent explosions.
Considering the pros and cons of pyrolysis, it’s clear that its benefits outweigh the risks. It’s a proven technology expected to grow by diverting waste tires that are landfilled or incinerated.
Tire pyrolysis at Contec
Contec’s pyrolysis process and technology have made it a leader in the industry for focusing on safety and sustainability.
The plant is checked regularly before starting each run and monitors the process constantly to ensure no pressure buildup could lead to an explosion. Contec’s Molten®, a molten salt and proprietary technology, has a high heat transfer exchange, so less energy is used. The molten salts are reusable, producing no pollutants when heated.
The design of modern waste tire pyrolysis plants results in reduced environmental impact, improved economic benefits, more safety for staff, and reduced energy costs. Companies like Contec are solving the growing waste tire problem and producing innovative recycled products without negative environmental or safety concerns.
Their innovations have adapted traditional pyrolysis technology to meet current environmental, sustainability, and ethical work standards while helping industries join the circular economy. Find out more about Contec’s circular TPO, ConPyro®.
If you liked reading this article, we recommend the following content:
Carbon black usage to sustainable opportunities
Disruptions to Carbon Black supply chains, rising costs of the fossil fuels used to produce Carbon Black, sustainability regulations, and stakeholder pressure have concerned industry leaders about the future of Carbon Black.
Luckily, more circular options are on the market, with similar properties to Carbon Black. Although they’re not directly replacing Carbon Black, these sustainable options have applications in many industries.
This article will teach you about the many recovered Carbon Black uses as a sustainable opportunity, especially as a feedstock for paints and inks.
What is recovered Carbon Black?
Recovered Carbon Black (rCB) is a solid residue from end-of-life tire (ELT) pyrolysis. Though rCB can be produced from various rubber waste, the billions of ELTs discarded annually provide a plentiful feedstock that would otherwise be treated as waste and end up in landfills.
Char is one of the tire pyrolysis products that is processed, milled, and pelletised to yield rCB. Industries manufacturing tires, inks, paints, coatings, and rubber that usually use virgin Carbon Blacks (vCBs) are opting for rCB. These industries find rCB is a sustainable choice capable of matching vCB properties and can help to overcome vCB supply bottlenecks and high costs. It’s also a more planet-conscious option that can meet consumer and industry demands for green products.
For example, the automotive industry is sourcing products made from recycled raw materials to make circular cars. Tire manufacturers incorporating rCBs into their tires can ensure that new cars are more sustainable and have a lower carbon footprint.
Similarly, the paints and coatings industries are adopting green chemistry and emphasising resource conservation by using products from alternate feedstocks instead of fossil fuels to minimise carbon emissions. Currently, 2 per cent of global fossil fuels are used to make ingredients for the paints and coatings industry.
Depletion of fossil fuels and concern over carbon emissions are driving the paints, inks, and coatings industries to look for sustainable opportunities. Instead of fossil fuels, rCB production uses ELTs as feedstock in pyrolysis, making rCB a circular option for vCBs made from fossil fuels.
Properties: recovered Carbon Black vs virgin Carbon Black
Despite its environmental and cost advantages, rCB is not a 1:1 replacement for any particular vCB grade.
rCB is a new, unique grade with its own properties. The American Society for Testing and Materials (ASTM) International workgroup 36, set up in 2017, is still developing quality standards for rCB. The properties of rCB include a mix of passenger and truck ELTs used in pyrolysis. Recovered Carbon black’s in-rubber properties are close to the vCB grades from N550 to N772, with N650 and N660 as the closest matches, found in significant quantities in tires of all vehicles. In coatings or plastics, rCB can substitute popular grades like N220 and N330.
However, minor amounts of high reinforcing vCB grades in tire components will also be part of rCB. Moreover, the chemicals and additives in waste tires will also make their way into rCB, affecting its properties.
The circular option: Recovered Carbon Black
rCB is a sustainable Carbon Black option because of its small carbon footprint and circularity.Contec’s rCB manufacturing process ensures 80 per cent less or 2 tonnes fewer carbon emissions per tonne of the product than vCB production. Whereas producing vCB requires 2 tonnes of sulphur-rich fossil fuels, 1 tonne of rCB can be made from just three ELTs.
The rCB’s low carbon footprint and circularity help industries comply with the environmental standards industries must now meet.
Tire producers can solve their waste problems and meet requirements set by the EU End-of-life Vehicles Directive using pyrolytic products.
The paints, inks, and coatings industries will find rCB valuable in reducing emissions as required by the Industrial Emissions Directive 2 2010/75/EU (IED) and its 2022 revisions covering chemicals production. The Directive regulates pollutant emissions (including greenhouse gases) and stipulates the use of Best Available Techniques to choose raw materials. The 2022 Commission to revise the IED supports improving resource use to build a low-carbon, clean, and circular economy.
Moreover, rCB’s low volatile organic carbon content and water-based formulations help the paints, inks, and coatings industries comply with REACH Regulation (EC 1907/2006) controlling the production and use of chemicals.
How is recovered Carbon Black made?
Around 20 to 30 types of pyrolysis processes exist, but not all are created equal. Conventional pyrolysis systems can’t guarantee consistency in the quality of rCB. Contec has improved the pyrolysis process with several innovations to make rCB of consistent quality.
What is pyrolysis? It’s a thermo-chemical process, and the technique is several decades old. While it has been used to recycle tire waste to recover materials for many years, market interest in the technology is new.
The tire rubber is separated from other components like steel, wires, and fabrics as part of the process and sent into a reactor. Contec uses its novel Molten technology to heat the shredded tires to temperatures up to 510°C in an oxygen-free atmosphere to decompose the complex polymers in tires into simpler components. The pyrolytic products of commercial interest are recovered gas, oil, Carbon Black, and steel.
What are common Carbon Black grades?
Carbon Black is a synthetic material made of 98 per cent carbon. Petroleum oil, gas, and coal tar are the common raw ingredients used to produce vCB through burning in reactors at very high temperatures to vaporise the carbon. After cooling, a paracrystalline spherical powder is made.
Different manufacturing processes and feedstocks produce varying particle sizes, surface area, and aggregate structure, which define the properties of the vCB. This means there are many grades of Carbon Black.
Most vCB grades stabilise and strengthen rubber products, but some also act as pigments:
- Grades with smaller particles, such as N110, N220, and N234, have high reinforcing, abrasion resistance, and tear strength. These grades are used as reinforcing filler materials to make rubber elastomers that form tire treads.
- Medium to high reinforcing grades like N330, N339, and N550 are found in tire treads, inner liners, carcasses, sidewalls, hoses, and extruded goods.
- Medium reinforcing vCB grades like N660 and N770 have low heat build-up and prevent tire deformation. They’re suitable for tire sidewalls, inner liners, and sealing rings. Other applications include hoses, extruded goods, cable jackets, footwear, floor mats, and mechanical goods.
- Low reinforcing vCBs like N990 have high loading capacity and elongation and are suitable for tire inner liners and belts, footwear, belts, hoses, mechanical goods, and wire insulation.
What are the uses of Carbon Black?
The tire industry consumes around 70 per cent of Carbon Black. Manufacturing other rubber products consumes around 20 per cent, with the remaining 10 per cent used for non-rubber applications. Carbon Black is used in many industries due to its potential uses as fillers, pigments, or UV protectants.
1. Fillers
Tire manufacturing uses most vCB grades as fillers to stabilise and strengthen rubber products, such as tire treads, sidewalls, tubes, belts, and carcasses. The cumulative effect of vCBs makes tires safer, longer lasting, and more durable for driving.
The vCBs comprise 21.5 per cent and 22 per cent of passenger and truck tires, respectively. The rCB’s properties make it a suitable replacement for several of these vCB fillers, reducing the carbon footprint significantly.
2. Pigments and For UV-Protection
Several vCB grades produce a wide range of pigments with good tinting, conductivity, and dispersibility properties, providing ultraviolet (UV) protection.
- The tire industry uses Carbon Black to protect tires from the harmful effects of UV light and ozone to extend tire lifespan.
- Inks, coatings, and paint manufacturers use Carbon Black to enhance the undertone and colour in many ink types, including toners for laser printers and screen inks. Coatings benefit from the Carbon Black’s high jetness, UV protection, and conductivity. High-performance coatings for aerospace, marine, wood, industrial, and decorative applications rely on Carbon Blacks.
- Plastic manufacturers add Carbon Black to industrial bags, refuse sacks, and household containers. The Carbon Black adds colour and provides UV protection to the plastic polymers making them thermal resistant. These properties are also essential for power cable insulations.
The use of fossil fuels to provide feedstock and energy for the manufacture of vCBs has increasingly become an image and compliance issue in all industries. rCB is a sustainable option to vCB for several of the above applications. Adding 10 to 30 per cent of rCB will often maintain the properties while reducing the negative environmental impact.
Common recovered circular products from ELTs
Each of these four recovered products has a place in the circular economy.
1. Recovered Carbon Black
Contec’s ConBlack® is a sustainable Carbon Black option, which can replace up to 30 per cent of semi-reinforcing vCBs, such as N550 and N660, to make new tires. ConBlack® can make inner liners, sidewalls, sealing rings, heavy-duty conveyors, transmission belts, and hoses. Adding up to 100 per cent of rCB can secure UV protection and produce non-tire items like rubber sheeting, roofing, cables, geomembranes, pigments, paints, inks, coatings, and plastic items.
2. Recovered gas
Gas is one of the first products formed in pyrolysis. Some condense into liquids during cooling, but the rest remains as gas, rich in hydrocarbons such as methane, butadiene, and butadiene. Contec has achieved self-sufficiency by using its recovered gas to heat the Szczecin plant.
3. Recovered Oil
Contec’s ConPyro® is the oil produced after refining and can equal virgin fossil fuels in quality. Sulphur and aromatic hydrocarbon-rich end-of-life tires derived pyrolysis oil (TDO) can replace fossil-based oil as feedstocks to produce high-reinforcing vCBs. These vCBs can further increase the proportion of recovered materials in tires.
4. Recovered steel
Contec’s ConWire® is retrieved before and after pyrolysis and can also be used again to produce new tires without losing quality. The tire, paints, coatings, ink, and plastic industries are considering various options, including biological materials and recycled products, as circular options to produce more sustainable Carbon Black options.
Manufacturers should consider using recovered Carbon Black
Recovered Carbon Black’s importance as a sustainable, circular raw material for several industries is growing.
In the tire manufacturing industry, rCB can offer a greener option. In the inks and paints industries, higher concentrations of rCB will be required to get the same pigment opacity levels as with vCB. However, the environmental benefits of rCB are considerable and outweigh the issues associated with making the switch.
Contec’s ConBlack® uses ELTs as feedstock and is asustainable and circular Carbon Black option to vCB because of its various proven uses and applications in several industries, from tire and rubber to paints, coatings, and inks. Get in touch to learn more about our sustainable solutions.
If you liked reading this article, we recommend the following content:
R&D’s contribution to circular manufacturing (and a sustainable future)
Environmental protection is becoming an important concern in manufacturing.
However, manufacturers do not have all the necessary viable technology to reach their Net Zero goals and help limit global warming to 1.5˚C. Therefore, R&D investments are being made to find circular solutions limiting carbon footprints, waste generation, and natural resource use in manufacturing.
This article will show how investing in R&D supports the circular model adoption — and how Contec is part of the story.
How to adopt the circular economy through R&D?
Knowing how to transition from a linear to a circular manufacturing business model can be challenging. Breaking down the process into small steps can make it easier to implement viable solutions. At Contec, we recommend breaking down this process into two steps.
Step 1: Determine carbon footprint and environmental impact
Manufacturers trying to reduce their environmental impact can start by establishing their current carbon emissions.
To do this, it’s important to calculate not only scope 1 and 2 emissions for each product but also scope 3 emissions:
- Scope 1 and 2 emissions come from company activities and energy sources.
- Scope 3 emissions cover a product’s entire value chain. These include emissions from manufacturing, processing, services, transporting raw materials, product packaging, transport, and media.
In some EU countries, it is also a requirement for companies to document data collection and testing for verification and transparency.
Step 2: Introduce a framework and standard for managing environmental impact
Companies should introduce a system for environmental management, like ISO 14001, if they don’t have one already.
They can incorporate their carbon footprint data into the system, which provides the structure needed for environmental improvements. These include formulating an environmental policy, planning, implementation, checking, and management review.
Most companies easily control Scope 1 and 2 emissions by replacing conventional energy with renewable sources. However, the complexities of Scope 3 emissions, accrued from other companies’ activities, make it harder to control them. For example, most emissions in tire manufacturing come from raw materials, like rubber and virgin Carbon Black (vCB), produced from fossil fuel-based feedstocks.
What other activities can R&D support?
R&D can help reduce the Scope 3 emissions of an entire value chain by providing innovative technological and material solutions.
Circular solutions such as recycling reduce natural resource use, associated carbon emissions, and the environmental impact of producing ingredients by making secondary raw materials from waste. It reduces waste landfilling and soil and water pollution. Moreover, circularity emphasises incorporating old material into new products, keeping it in circulation.
For example, tire manufacturers can get high-quality recovered Carbon Black (rCB) from pyrolysis using Molten technology. Molten allows for uniform and regulated heating of tire wastes to produce rCB of high and consistent quality. This rCB can replace 20 per cent of medium-grade vCB. Molten technology uses less energy to produce secondary raw materials, reducing production emissions.
rCB’s carbon footprint is only 20 per cent of vCB’s. Tire manufacturers can use rCB in a tire-to-tire business model to diminish Scope 3 emissions. Thus, an innovation like Contec’s Molten technology integrated into an old process like pyrolysis can become a game changer for the entire tire industry.
Evolving the R&D at Contec
Every technology is the result of detailed research. However, a manufacturing operation can’t be changed before its influence on the process and product quality is identified. For this, it’s necessary to have standards to establish product quality and correlate new applications with product parameters.
These standards are created by more investment in R&D.
Contec’s pyrolysis process is rooted in R&D. Molten technology was incorporated into tire pyrolysis during laboratory testing and was found to improve the efficiency and safety of tire pyrolysis for people and the environment.
Next, Contec aimed to scale up the innovation and upgrade the tire pyrolysis plant to achieve nominal capacity. Due to an absence of ready-made technological solutions, Contec built its own laboratory facilities and tested the effect of every technology process change on product quality. Complete control over the research process and cooperation with technical universities make Contec’s R&D process unique.
Since there were no existing rCB quality standards, Contec joined the ASTM Committee D36 to contribute to formulating quality standards and testing methods for rCB. The company leverages its knowledge over years of R&D to improve product quality.
The Circular Economy is not possible without R&D
R&D can enable the development of environmentally friendly technologies for the circular economy by supporting the environmental impact verification of new recycled products.
A company with its R&D laboratory can shorten the validation process through monitoring and rapid course corrections. The flexibility to customise tests for specific needs helps to create products suited for market needs and gives a company a competitive edge. Cooperation with research institutions increases access to scientific expertise and improves fund-raising possibilities. Follow our Linkedin Page to learn how the latest R&D advancements.
If you liked reading this article, we recommend the following content:
Rubber and beyond: What are tires made of?
As manufacturers move toward the circular economy, they’re increasing the use of recycled materials.
In the tire and automotive industry, one of the solutions is to extract raw materials from recycled tires to produce new tires with a higher percentage of recycled materials.
Contec is one of the supporters of this movement toward circularity, supplying raw materials from recycled tires and allowing manufacturers to keep resources circulating within the industry.
However, tires are complex products, and to fully understand how a tire-to-tire circular model can function properly, it’s essential to know the composition and components of the tires.
Let’s start with understanding the composition of tires: what are they made of?
What are tires made of?
Tires are complex structures made of rubber, steel, and fabric components. Rubber is the primary material in any tire, and four main types of rubber are used in various tire components (Grammeli).
The primary source of natural rubber is Hevea trees (or rubber trees), whose latex is about 40 per cent rubber. The rubber is extracted by coagulating the latex with formic acid. Natural rubber is self-reinforcing and has high mechanical strength and medium elasticity but has low viscosity and other disadvantages.
Natural rubber needs further treatments before it can be used in tire manufacturing, such as vulcanisation, mixing with Carbon Black fillers, and other processes (Deng).
Due to the high cost and scarcity of natural rubber, synthetic rubber polymers produced from fossil-fuel-based hydrocarbons are also used (Deng). All synthetic rubbers are highly elastic and have good wear resistance, but variations in heat generation and hysteretic loss exist. There are four main types of synthetic rubber:
- Styrene Butadiene Rubber
- Polybutadiene Rubber
- Isobutylene-isoprene Rubber
- Isobutylene-isoprene Halogenated Rubber
In tire manufacturing, synthetic and natural rubber are cut and mixed in fixed ratios with other ingredients.
Different recipes or precise mixes of materials produce tires with unique properties suitable for diverse vehicles. Moreover, tire rubber composition can differ based on national or regional regulations (Grammelis), as shown in Table 1.
Composition of tires: beyond rubber
Even though rubber is the primary component in any tire, it’s essential to recognise that tires are complex products, and their composition extends to many other materials that vary according to their use and country of origin.
Besides rubber, the different materials in a tire are steel, textiles, fillers, and chemical additives required for structure, strength, longevity, and durability, as we can see in the table below:
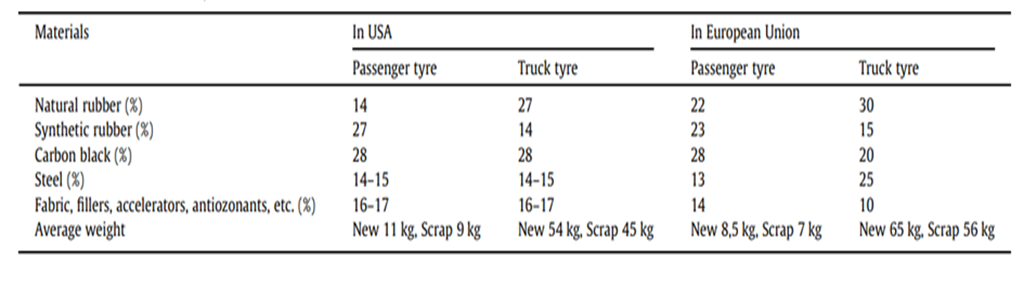
Table 1: The composition of tires from different regions will vary. Materials are listed according to the percentage of the total tire weight. (Credits: Progress in used tyres management in the European Union: A review)
Let’s look at each tire component in more detail:
- Rubber (natural and synthetic) comprises 41-45 per cent of tire materials and has structural and strain functions. Rubber determines tread tensile and tear strength, elasticity, and elongation. Truck tires have more natural rubber, and car tires have more synthetic rubber. Trucks carry heavy loads and travel intensively, so the tires are subject to wear and tear. Natural rubber’s abrasion properties are superior to synthetic rubber, so more natural rubber is used for trucks. A higher proportion of synthetic rubber is enough for less wear and tear in car tires due to lower load and mileage.
- Fillers make up nearly 30 per cent of tire materials. Fillers such as Carbon Black, silica, carbon, and chalk, among others, are reinforcing materials. Different fillers provide varying tire strength, wear resistance, tear resistance, rolling resistance, puncture resistance, etc.
- Steel makes up 13-25 per cent of tires, and as part of belts, beads, and plies act as a structural skeleton.
- Textiles (polyester, rayon, nylon) as fabric cords comprise around 5-15 per cent of tires and provide structure and reinforcement.
- Antioxidants, antiozonants, plasticisers, and curing chemicals comprise the remainder. The substances and percentage of these minor ingredients depend on each manufacturer.
Antioxidants like phenols and secondary naphthylamines protect against the effects of temperature and oxygen, and antiozonants shield tires against ozone. Curing chemicals like sulphur, zinc, lead, magnesium, and cadmium oxide are used for vulcanisation. Plasticisers, such as oils and resins, are added to the rubber mixture to reduce friction in the tire.
Differences in tire composition will affect the nature of secondary material recovered after recycling.
Tire recyclers like Contec have a strict truck-to-passenger-tires ratio to maintain consistency in their product profile and characteristics of products like medium-grade recovered Carbon Black (rCB). However, it’s still challenging to standardise rCB since the tires produced in different regions have varying quality and properties due to regional tire composition variations.
Contec’s involvement with ASTM International is important to developing industry rCB standards and industry applications. Learn more about our involvement in ASTM.
What are the main parts of a tire?
The main parts of a tire are the bead, bead filler, inner liner, carcass, sidewall, belts, and tread—you can see it in detail in the image below.
Bear in mind that, depending on the type of tire, there can be more components.

Figure 1: Tire structure. (Credits: What is in a Tire)
The various components used in making a tire are also crucial for material recovery. Several materials can go into making a single component depending on its function. Let’s discuss some components common to all tires below:
- Bead has steel cord in rubber bundles to secure the tire to the wheel rim and prevent wear and tear by rubbing against the edge.
- Bead Filler is a synthetic rubber component wrapped on the top and around the bead and between body plies to tune the ride.
- Innerliner is made of butyl rubber and is necessary to maintain inflation pressure.
- Carcass or body ply is made of textile, fiberglass, and aramid cords to retain tire shape and prevent the tire from bursting during inflation.
- Sidewall is made of natural rubber, protects the carcass, and can withstand bending and aging.
- Belts are composed of steel cords encased in rubber. Belts prevent carcass damage, stabilise the tread, and reduce rolling resistance.
- Tread and tread patterns can have synthetic or natural rubber, depending on their use. It’s the part that comes in contact with the road and provides grip and abrasion resistance.
The cross-linked nature of rubber structures with other materials like fabrics or steel makes recycling challenging, as the different components and materials must be separated before processing.
How are tires manufactured?
Tire manufacturing is a complex process. Each tire manufacturer follows unique and proven procedures, from raw materials selection to quality management.
There are five main stages in tire manufacturing, which, according to Weyessenhoff, are as follows:
- Sourcing good quality material: The first step in tire manufacturing. Choosing reliable and standardised recycled secondary materials allows manufacturers to make tires circular. Manufacturers can get recovered medium-grade Carbon Black, recovered steel, and feedstocks to produce fine-grade virgin Carbon Black. They can also source carbon materials and chemical additives from other recycled biological materials. Choosing materials depends on their properties and interactions with each other because the end goal is to produce a strong and stable tire. The mixed chemical composition makes tires resistant to decomposition by chemicals or high temperatures during recycling.
- Manufacturing components: A step that requires mixing different materials to produce various tire components. For example, steel cords and rubber for beads, etc.
- Tire assembly: This is the stage where the components of prepared belts are wound and glued together. The end-product of this confectioning stage is called a “green tire.”
- Vulcanisation: This step completes the process and gives the tires their final shape, including the tread and its patterns. Since the EU stipulates that the minimum tread groove is at 1.6 mm, some manufacturers add a tread depth indicator: 3 mm for summer tires and 4 mm for winter tires.
- Quality control: Tires must pass quality tests to meet stringent safety standards (UNECE, SAE). Improper quality control during manufacturing can produce hidden defects in materials and tires. Most of these tend to occur at the interface of different materials and can be at the shoulder, internal, external, side, or tread. Quality checks during manufacturing are vital to reducing user risks and financial burdens on customers and producers.
Other questions on how a tire is made
Here are answers to three FAQs for a quick and brief understanding of the multifaceted tire manufacturing process.
Where does rubber come from for tires?
The latex of a tropical tree, Hevea brasiliensis, also known as the “rubber tree”, is the source of natural rubber used in tires.
Around 90 per cent is obtained from Asian plantations. The tire industry is the largest consumer of natural rubber, using 76 per cent of the annual rubber production. The rubber tree is currently the only commercial source of natural rubber, though efforts are being made to identify other easily renewable crops or wildflowers like dandelions to produce rubber.
The four types of synthetic rubber made from hydrocarbons derived from petroleum products are mixed with natural rubber to make tires.
What is used to make tires?
Tires are made of several materials, including natural rubber, synthetic rubber, steel, textiles (rayon, polyester, aramid, and nylon), fillers (carbon black, silica from sand, carbon), chemicals including hazardous compounds like lead and cadmium oxide, and fossil fuels as feedstock for producing many of the synthetic materials.
Are tires made of natural rubber?
Tires are made of natural rubber.
Aviation tires are made entirely of natural rubber as they withstand abrasion better than synthetic rubber. For the same reason, trucks and heavy vehicles also have more natural rubber in their tires. Passengers or light vehicles have more synthetic rubber. Due to the scarcity of natural rubber, synthetic rubber use is high, making up around 60 per cent of tire rubber, while natural rubber makes up about 40 per cent.
Adding recycled materials to tire composition
Manufacturers want to maximise circularity in tires. Therefore, tire manufacturing, especially the sourcing and assembly stages, is undergoing a paradigm shift to fit a circular economy.
Besides recycling and sourcing bio-based renewable materials for significant tire components, manufacturers are also rethinking tire design to make disassembly, material separation, and recycling easier to reduce tire waste.
Contec has one of the few tire pyrolysis plants where they recover 85 per cent of the material in tires and 15 per cent of energy to tackle the growing end-of-life tire waste problem. Contec is promoting tire-to-tire production by providing manufacturers with rCB, recovered steel, and feedstocks to realise manufacturers’ vision.
If you liked reading this article, we recommend the following content:
Contec raises largest Clean Tech investment in Europe
Our funding round now reaches EUR 15 million — one of 2023’s largest Clean Tech investments in Europe.
The largest Polish manufacturer of steel roofing and facades – Pruszyński – has contributed an additional EUR 5 million to the funds already provided by VINCI and the Warsaw Equity Group. These two entities had initially invested EUR 10 million in Contec back in March 2023.

The investment will be used to triple the capacity of Contec’s current facility in Szczecin, Poland, and to position the company for the construction of several new commercial plants across Europe. This will support Contec’s mission to accelerate the transformation of the manufacturing industry toward carbon neutrality.
For many years, we have been supporting the efforts of the manufacturing sector to promote environmental sustainability and circularity. Contec’s circular products significantly reduce the carbon footprint by more than five times compared to traditional fossil fuel-based raw materials. That’s why there is a great deal of interest in Recovered Carbon Black for the tire, manufactured rubber goods, plastics, and pigment industries. – Krzysztof Wróblewski, CEO of Contec.
Thank you to our investors and the entire team for making this milestone possible!
To read the full press release, please download it as a PDF .
For media inquiries, please reach out to Anna Goławska <a.golawska@contec.tech>.